By Brandi Buzzard on August 18, 2022
The Different Types of Cattle Operations
The Beef Lifecycle: Putting Together the Pieces

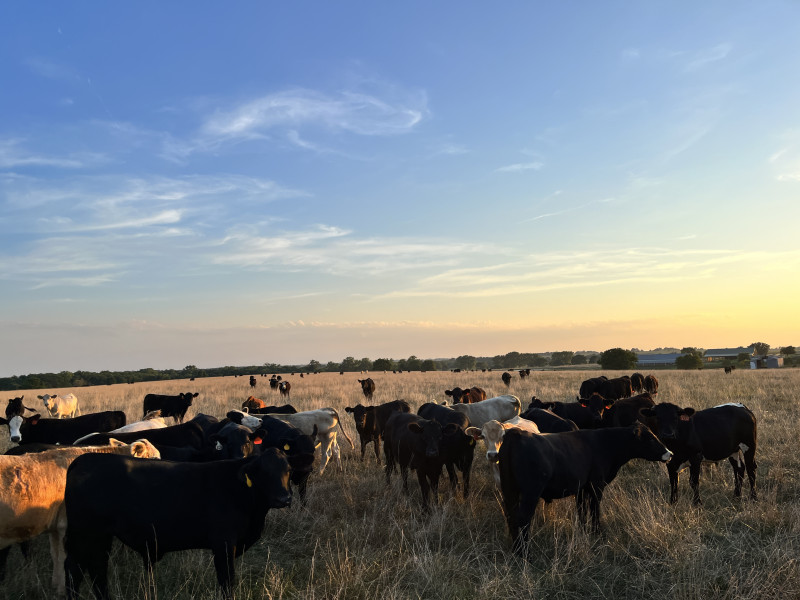
There are a lot of people in the beef community who bring beef from pasture to plate. And while we talk about ourselves as just farmers and ranchers, the beef community is a bit more complex than that. Sure, we all raise cattle and help produce beef for a hungry nation (and world) but the way we raise cattle on my ranch is different from my neighbors’ ranch, which is different from the next neighbor down the road, etc.
Cow-Calf Operation
For example, we are primarily a cow-calf ranch which means we have a herd of cows that will have calves and once those calves are approximately seven months old, they will be weaned from the cows and can go one of two ways – they can be funneled into the beef supply as “stockers” (which I’ll discuss next) or raised as purebred bulls or heifers (young females) to be sold to other cattle producers. Both options are dependent on factors such as weather, resource availability and the market – and all of those factors can change from month to month.
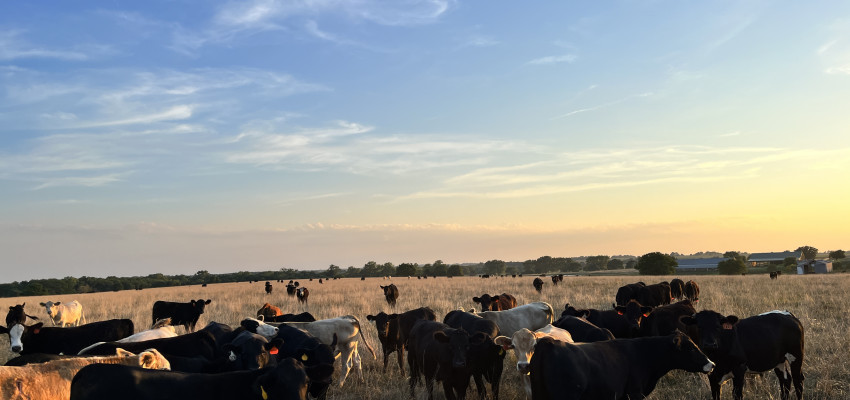
 Stocker Cattle
Stocker Cattle
If our weaned calves don’t have the optimal combination of structure and genetics to qualify for purebred cattle sales, they move on as stockers, which is the next phase of the beef lifecycle. The stocker phase comes after weaning but prior to cattle being fed to harvest weight at a feedyard and is simply several months of grazing on grass, sometimes with a protein supplement (depending on the availability of forage such as grass and/or hay). In a year like 2022, drought is widespread across the nation, so pastures are short on grass. This translates to a decrease in hay available for feeding. Many farmers and ranchers are being forced to make tough decisions about herd reduction, feed availability and marketing options.
Finishing Cattle at a Feedyard or On the Ranch
After the stockers graze and gain weight for several months, they then move to the “finishing” stage of the lifecycle. It’s common for finishing – the process of putting muscle and fat on a beef animal – to take place in a feedyard. However, this phase can also happen in a pasture or dirt lot with grass-finished cattle, too. Additionally, some producers will “finish” cattle at their own homes, either to process for beef for their own families or to sell to local consumers who wish to purchase beef straight off the farm or ranch. Our ranch is one that sells some beef in this manner, providing us with another marketing opportunity for our cattle if other markets aren’t favorable.
Processing Stage for Consumption
After reaching harvest weight, the cattle are sold to a meat processing company and the beef meets its final destination on our breakfast, lunch and supper tables.
You might read this and think, “Well, that wasn’t too complex” but there are hundreds of ways to raise cattle, and it varies from farm to ranch, county to county and state to state. For example, some cattle owners buy a small herd of bred cows, keep them long enough to have calves, then sell the whole herd as a pair. Specialization enables cattle owners to find new profit avenues while contributing to the beef supply in their own way. Regardless of how a producer participates in the beef lifecycle, you can be confident the beef in the grocery store and at your local butcher shop is nutritious and safe for your family.